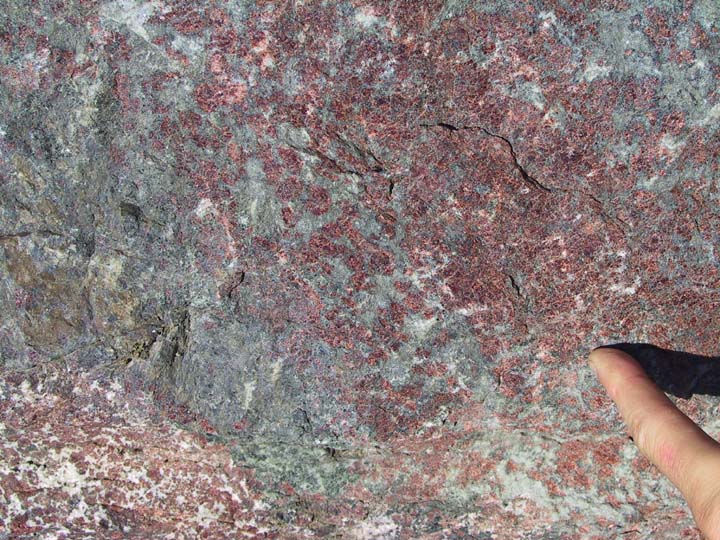
- Celsius, °C, uses 0°C for ice + water at 1 atm, 100°C for water + steam at 1 atm
- Kelvin, K, uses 0 K for absolute zero; K = °C + 273 (e.g., room temperature is 298K or 25°C)
the change in the amount of heat that a material contains is related to its heat capacity CP and the temperature change dT:
- dq = CP dT
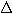 T =
T = 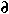 T /
T / 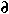 z
z
change in temperature T with depth z
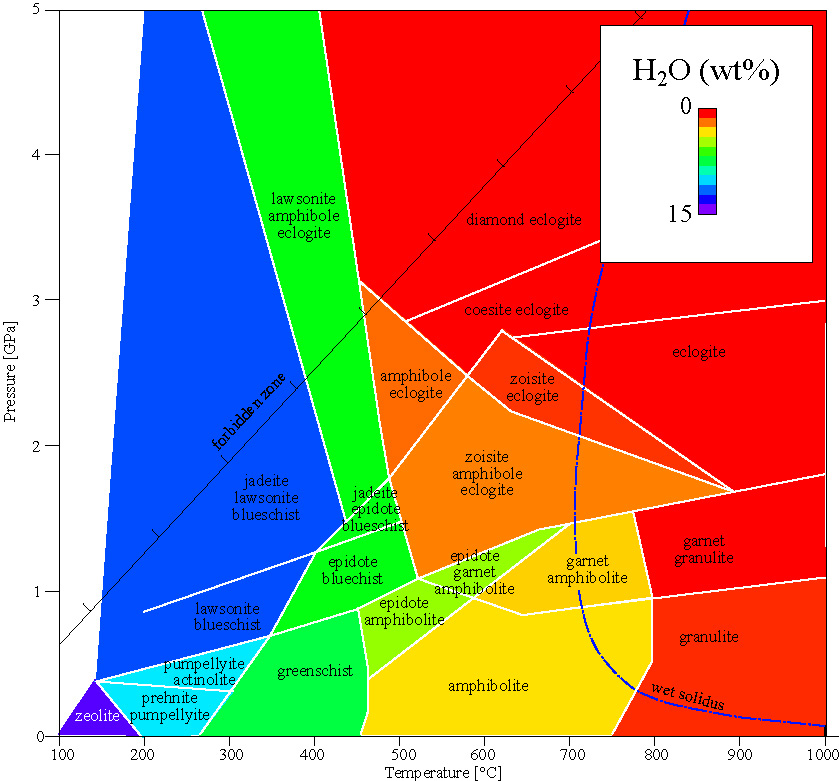
= 5-10 K/km in cold subduction zones
= 20 K/km in stable cratons
= 50 K/km in rifts and magmatic arcs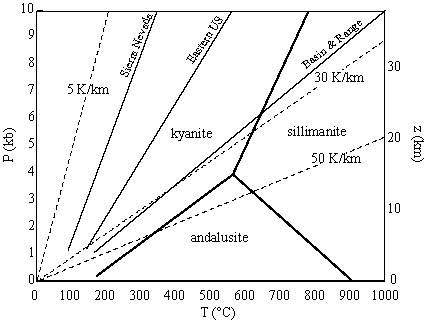
The heat of the Earth was produced by its early accretion and continues to be produced by the crystallization of the inner core from the outer core (remember that melting requires heat, so crystallization must give off heat), and the radioactive decay of unstable isotopes or radionuclides (chiefly the decay schemes 235U —> 207Pb, 238U —> 206Pb, 40K —> 40Ar, and 232Th —> 208Pb)
Three processes transfer heat in the Earth:
- conduction: the transfer of heat by molecular
vibration. Fourier's law states that the heat flux q (flow of heat per
unit area and per unit time) is:
- q = k
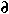 T /
T / 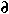 z
z
View diffusion A rough measure of the distance that a thermal pulse can travel in a specific time (or the amount of time required for a thermal pulse to travel a certain distance) is given by the characteristic diffusion distance: - q = k
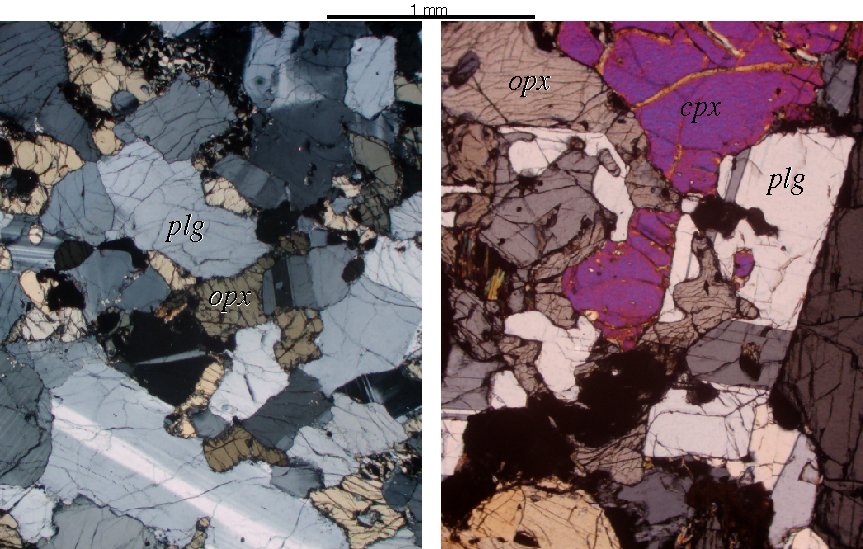
- advection: the transfer of heat by motion of rocks
e.g., cold rock is carried deeper in subduction zones
e.g., hot rock is carried upward in dikes
- convection: the transfer of heat by buoyancy-driven circulation
Example: as rock in the lower mantle is heated, its density decreases because of thermal expansion, and it rises; as rock in the upper mantle cools, its density increases, and it sinks.
Example: when new magma is injected into a magma chamber, its density is lower than the cooler bulk of the magma chamber, so it rises, while the cooler magma in the chamber sinks.
Arthur Holmes realized as early as 1931 that thermal convection in the mantle drives the plate tectonics of the Earth
convection accounts for about 6X more heat transfer in the mantle than conduction (this ratio of convection to conduction is called the Nusselt number)
View convection
Within a convecting cell,
temperature is nearly constant, following an adiabat. At the edge of
the cell is a thermal boundary layer where convection changes to
conduction. This discontinuity defines the transition between the
asthenosphere and lithosphere in Earth.
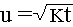
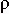 g z
g z
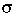 ii =
ii =