Geology 2 Spring 1997
Name:
Lab day & time:
PRELAB #5. STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY
This prelab assignment is due at the beginning of your lab session. You will not be allowed to participate in the lab if you have not completed this prelab exercise.
Read Chapter 9 in Chernicoff and answer the following questions.
1. In a few words, describe each of the following
types of deformation (page 162)
.
a.
elastic deformation
b.
brittle failure
c.
plastic deformation
Which type of
permanent deformation (plastic or brittle) would you expect to occur in
the following environments?
a) Near-surface deformation (an environment with relatively low temperature and relatively low lithostatic pressure)
b) Deformation at great depths with high temperature and high lithostatic pressure
2. What does the principle of original horizontality say? (page 145)
If a geologist finds sedimentary rock beds in the field that are not now horizontal, what is s/he likely to conclude?
3. Define the terms
strike and
dip. (page 163)
Geologists describing sedimentary rock beds that they find in the field are constantly measuring and recording their strikes and dips. Why do you suppose these are such important measurements?
4. What does the
principle of superposition say? (page 145)
5. Draw a
cross-sectional view of some folded sedimentary beds (pages 164-165). Label each
fold limb and
fold axis, and tell whether each is a
syncline or an
anticline
.
Imagine that the tops of your folds have been eroded, like those in Figure 9-6, page 164, for example. Imagine you are walking along on that ground surface, observing the various rock layers.
When you come to the axis of an anticline, are the rocks in the center of the fold older or younger
than the rocks on either side (i.e., those forming the limbs of the fold)?
Older or younger?
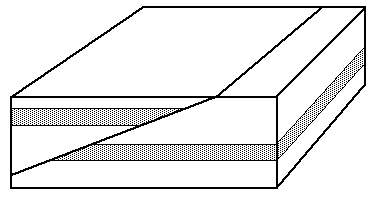
6. Check out the
fault shown in the
block diagram, below.
Is it primarily a
dip-slip fault or a
strike-slip fault? (page 169)
Is it a
normal fault,
reverse fault,
thrust fault, or
strike-slip fault?
On the diagram, label the
hanging wall, the
footwall, and the
fault plane.
Name the plate boundary between the North American and
Pacific Plates (that lies in coastal California)
What kind of fault is it?
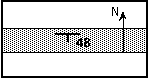
For the bed shown below in map view, describe what is meant by the
strike and dip symbol
The beds strike in what direction?
The beds dip how many degrees?
Do they dip to the
N or
S (circle one)